Frequently Asked Questions
HPLC
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is performed using an HP Agilent 1200 system equipped with a Diode Array Detector (DAD) for UV-Visible wavelength detection. The system utilizes a reverse-phase C18 column for peptide analysis, with samples filtered before injection to ensure accurate separation and system integrity.
- How is quantification performed?
- Calibration curves are generated using certified reference standards, establishing a linear relationship between concentration and peak area. This ensures precise and reliable quantification of target compounds.
- How were your methods established?
- Our methods are developed and validated by a credentialed scientist, following best practices and industry guidelines. Reproducibility is ensured through:
- Strict Protocol Adherence – Standardized procedures maintain consistency and accuracy across all analyses.
- Quality Controls – Reference standards are analyzed with each sample to verify retention time consistency, peak resolution, and system repeatability before analysis.
- Our methods are developed and validated by a credentialed scientist, following best practices and industry guidelines. Reproducibility is ensured through:
Cultures
Total Aerobic Microbial Count (TAMC) and Total Yeast and Mold Count (TYMC) testing is performed following USP <61> guidelines. Aseptic technique is used inside a HEPA-filtered biosafety cabinet with sterile materials to minimize the risk of contamination and false positives.
Samples are plated on two agar types designed to support the growth of a broad range of bacteria, yeast, and mold for sterility testing. Agar plates are incubated at 30°C for 10 days to allow sufficient time for microbial growth. A “Pass” result is indicated by 0 Colony-Forming Units (CFUs) after the incubation period.
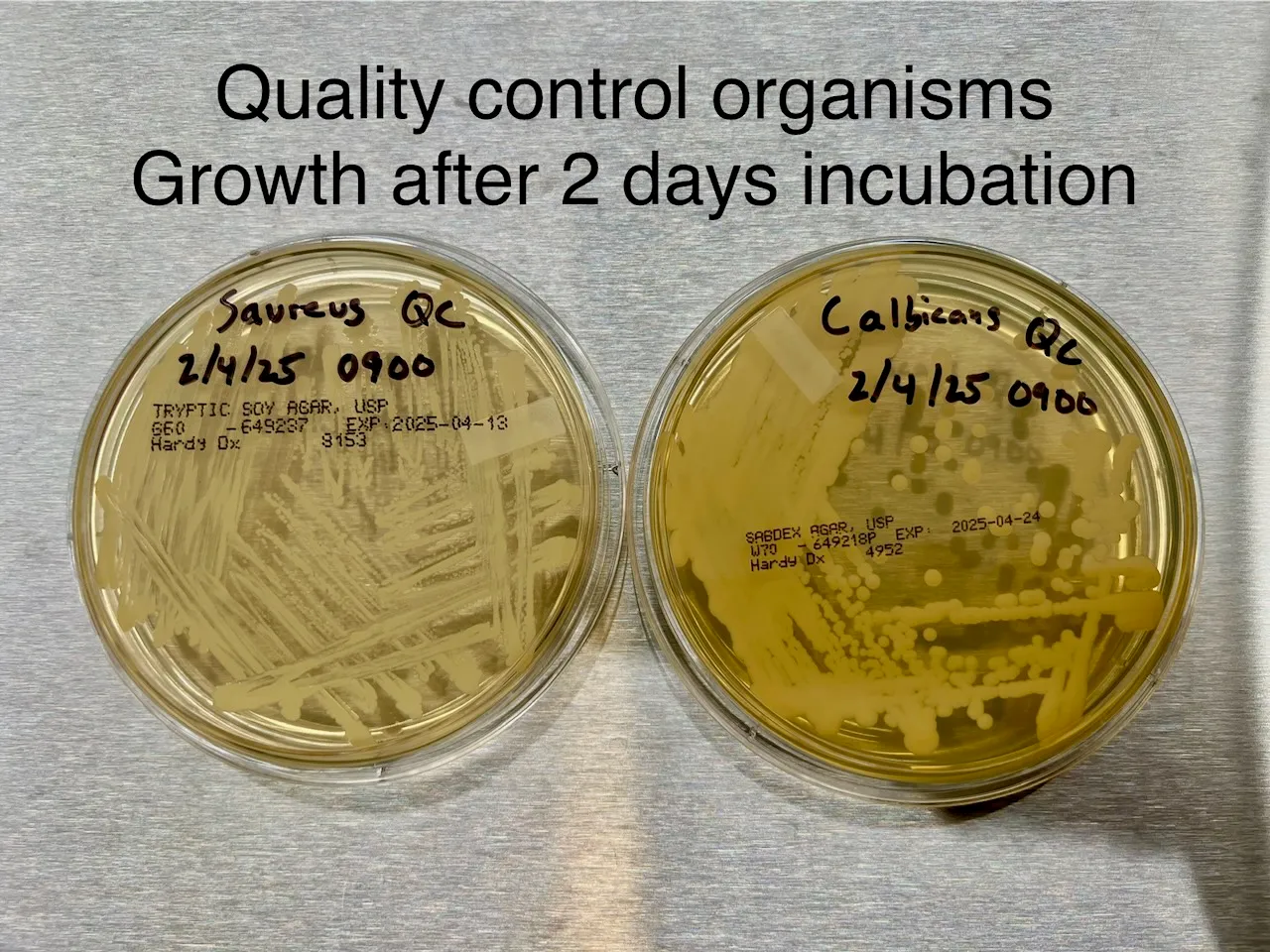
To ensure accuracy, positive quality control organisms are tested on each batch of agar plates to confirm their ability to support microbial growth.
Example positive quality control images: Top, Bottom
- Why are cultures incubated for 10 days?
- In clinical microbiology, aerobic cultures are typically incubated for 3 days, anaerobic cultures for 5 days, and mold cultures for 10 days. We use a 10-day incubation period to allow sufficient time for slow-growing organisms to become detectable, ensuring an accurate sterility assessment.
- How do you confirm a sample is negative?
- A sample is considered negative if no microbial growth is observed after 10 days of incubation. To validate this process, samples are handled under the same conditions as quality control tests, which consistently demonstrate growth when viable organisms are present.
pH
Testing is performed using a lab-grade pH electrode calibrated with three standard buffer solutions to ensure accuracy and reliability. 0.5 mL sterile water
- Why is it important to use a lab-grade pH meter?
- A high-quality pH meter provides greater accuracy, stability, and traceability to National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) reference materials.
- What are standard buffer solutions?
- Standard buffer solutions are precisely formulated reference solutions used to calibrate pH meters. Using three-point calibration helps correct meter errors, ensuring accuracy within ±0.02 pH units.
Supplemental
Figure 1
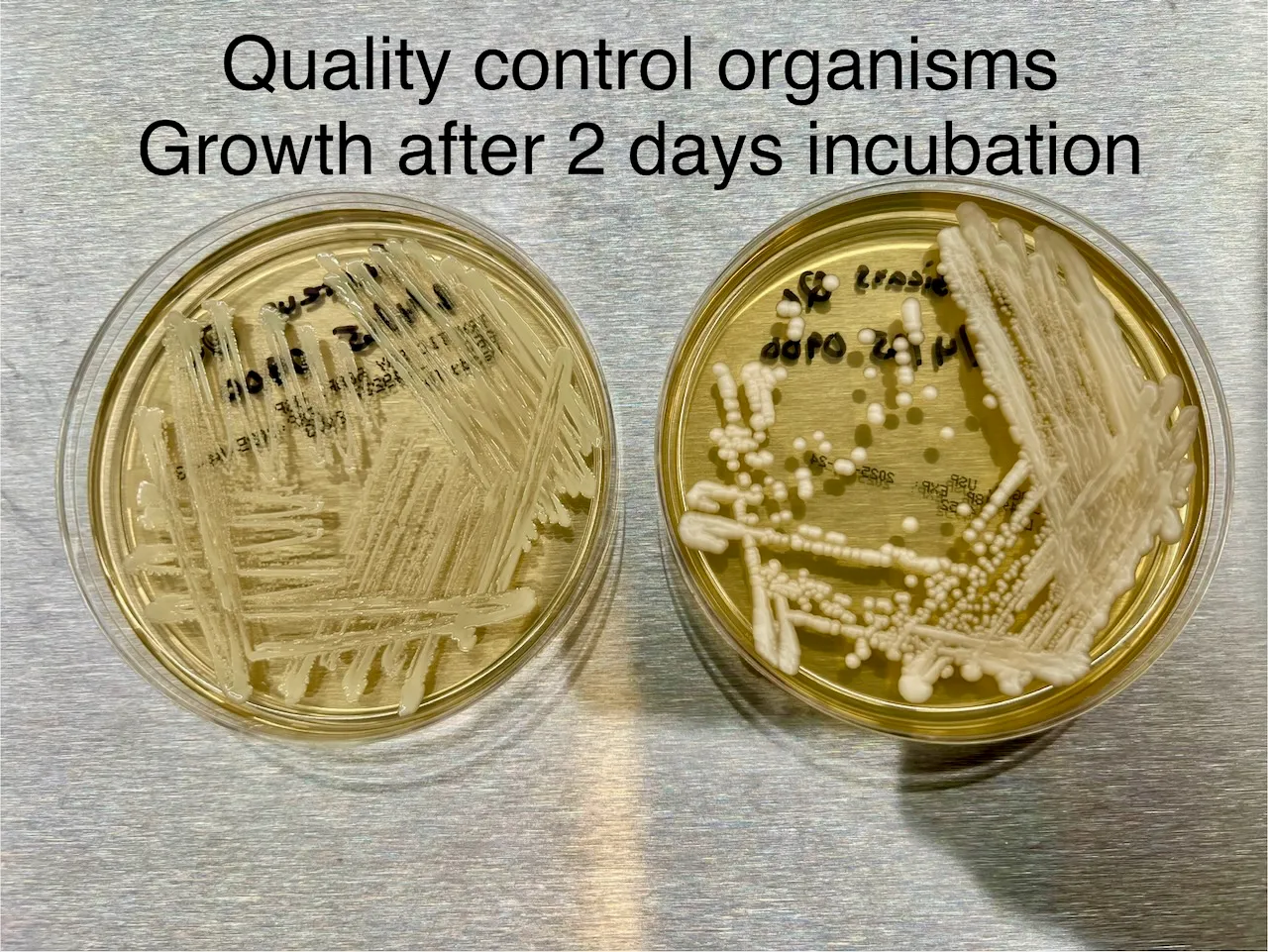
Figure 2